Contents
- Airship
- Calico
- Camunda
- CI
- CD
- Ceph
- CNI
- Gerrit
- Jenkins
- JIRA
- Kubernetes
- NARAD
- Nexus 3
- ONAP
- OpenStack
- OVS-DPDK
- PINC
- Shaker
- SonarQube
- Sonobuoy
- SR-IOV
- Tempest
- Yardstick
Airship
A collection of inter-operable and loosely coupled open source tools that provide automated cloud provisioning and management in a declarative way.
Airship helps operators take control of their infrastructure, by providing a declarative framework for defining and managing the life cycle of open infrastructure tools and the hardware below. These tools include OpenStack for Virtual Machines, Kubernetes for container orchestration, and MaaS for bare metal, with support for OpenStack Ironic on the way.
Read the documentation.
Source: AT&T
Calico
A new approach to virtual networking and network security for containers, VMs, and bare metal services.
Calico provides a rich set of security enforcement capabilities running on top of a highly scalable and efficient virtual network fabric. Calico includes pre-integration with Kubernetes and Mesos (as a CNI network plugin), Docker (as a libnetwork plugin) and OpenStack (as a Neutron plugin). Calico supports a broad range of deployment options including on premise or public cloud (AWS, GCE, etc) providing the same rich set of features across all.
Calico's network policy enforcement ensures that the only packets that flow to/from a workload are the ones the developer or operater expects. This is achieved by mapping high-level developer/operator intent to fully distributed ACLs running on every host. You can think of Calico as providing every workload with a fully automated virtual firewall to protect the workload and to protect the rest of your application should that workload become compromised. Calico automatically maps any network policy concepts from the orchetration envirnoment into Calico network policy. (For example, Calico was selected as the reference implementation of network policy for Kubernetes.) Calico network policy can also be specified using the Calico command line tools and APIs, either in place of or augmenting the policy concepts provided by the orchestration system.
Calico's highly scalable network fabric is built using the same principles as the internet - the most highly scaled network in existence. In contrast to most virtual networking solutions, Calico provides a flat IP network that can typically be run without any encapsulation (no overlays). The ability to run without an overlay provides exceptional throughput characteristics, and for large scale service operators makes diagnosing network connectivity issues a breeze. In addition Calico's network fabric also includes the ability to route packets using a stateless IP-in-IP overlay for any scenarios where an overlay network might be preferred.
Calico's network policy enforcement can also be combined with other virtual networking solutions. For example, the Canal project adds Calico policy enforcement to Flannel virtual networking. This exciting project brings rich network policy to Flannel users, and brings more network connectivity options to Calico users.
Read the Version 1.6 documentation.
Source: Calico
Camunda
A light-weight, open-source platform for Business Process Management.
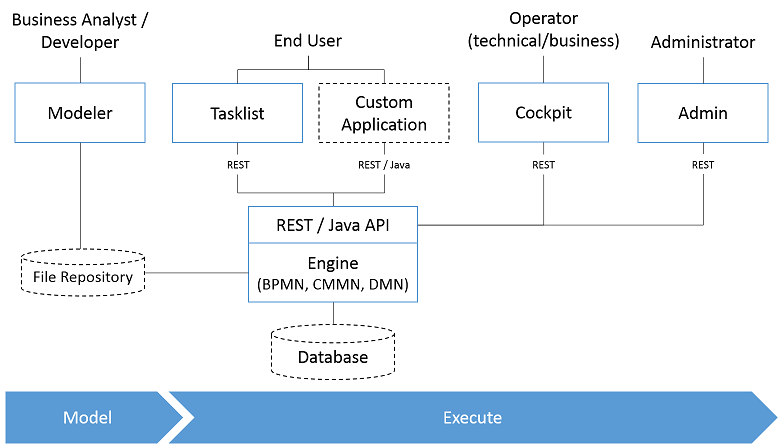
Camunda is a Java-based framework supporting BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) for workflow and process automation.
The following figure shows the most important components:
Continuous Delivery (CD) is a DevOps software development practice where code changes are automatically built, tested, and prepared for a release to production.
Continuous Delivery expands upon continuous integration by deploying all code changes to a testing environment and/or a production environment after the build stage. When continuous delivery is implemented properly, developers will always have a deployment-ready build artifact that has passed through a standardized test process.
Continuous delivery lets developers automate testing beyond just unit tests so they can verify application updates across multiple dimensions before deploying to customers. These tests may include UI testing, load testing, integration testing, API reliability testing, etc. This helps developers more thoroughly validate updates and pre-emptively discover issues. With the cloud, it is easy and cost-effective to automate the creation and replication of multiple environments for testing, which was previously difficult to do on-premises.
Source: AWS
Ceph
A unified, distributed storage system designed for performance, reliability and scalability.
Ceph delivers object, block, and file storage in one unified system.
Read the documentation.
Source: Ceph
CNI
Container Network Interface (CNI), a Cloud Native Computing Foundation project.
CNI consists of a specification and libraries for writing plugins to configure network interfaces in Linux containers, along with a number of supported plugins. CNI concerns itself only with network connectivity of containers and removing allocated resources when the container is deleted. Because of this focus, CNI has a wide range of support and the specification is simple to implement.
Source: Cloud Native Computing Foundation Project.
Gerrit
Gerrit is used for code review. Gerrit is built using the secure postsql db utility. It allows developers to push code into a legitimate vault, where it can be reviewed, and deployed into the production environment. Gerrit also fully synchronizes with git.
Jenkins
A Jenkins container automates the CI process. This container contains the necessary Gerrit and Nexus plugins to build jobs that will run unit tests, execute static source code analysis, and deploy build artifacts to Nexus.
JIRA
JIRA tracks Akraino code, feature, and overall project-related issues, affording the opportunity for users to report issues in a timely manner and track their resolution per agreed timelines.
Kubernetes
(Commonly stylized as K8s) An open-source system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
Kubernetes groups containers that make up an application into logical units for easy management and discovery. Kubernetes provides a container-centric management environment. It orchestrates computing, networking, and storage infrastructure on behalf of user workloads.
Read the documentation.
Source: Kubernetes
NARAD
Network Augmentation Resource Automation Database (NARAD), a data model approach to network cloud infrastructure.
NARAD:
- Provides a common database for infrastructure
- Is the DBOR (database of record)
- Hosts all components of the data model
- Exposes a uniform API
- Implements data integrity and validation rules
Source: AT&T
Nexus 3
Nexus 3 supports both repositories and containers. It is integrated with Jenkins, publishing both artifacts and Docker containers. The Maven build uses Nexus 3 as a proxy repository for third party libraries. Afterward, built and packaged artifacts are posted in the Nexus release repository for downloading.
ONAP
Open Networking Automation Platform (ONAP), a comprehensive platform for real-time, policy-driven orchestration and automation of physical and virtual network functions.
ONAP will enable software, network, IT and cloud providers and developers to rapidly automate new services and support complete life-cycle management.
Source: ONAP
OpenStack
Open source software for creating private and public clouds.
Read the documentation.
OVS-DPDK
Open vSwitch with Data Plane Development Kit (OVS-DPDK), a high performance open source virtual switch.
Open vSwitch is a multi-layer virtual switch licensed under the open source Apache* 2.0 license. It supports SDN control semantics via the OpenFlow* protocol and its OVSDB management interface. It is available from openvswitch.org, GitHub, and is also consumable through Linux distributions. DPDK is a set of user space libraries that enable a user to create optimized performant packet processing applications (information available at DPDK.org). In practice, it offers a series of Poll Mode Drivers (PMDs), which enable direct transferral of packets between user space and the physical interface, bypassing the kernel network stack.
Source: Intel
PINC
Platform for Intelligent Network Control (PINC), provides the ecosystem for Network Fabric Configuration Automation.
Features:
- Powered by SDN-F, that uses the ECOM SDN-Controller base
- Uses a model based configuration paradigm and reverse mapping methodologies to insulate the service from device specifics
PINC handles fabric configuration by compartmentalizing the configuration application into the following stages:
- Bootstrap Configuration
- Base Configuration
- Base Incremental
- Dynamic Configuration
Source: AT&T
Shaker
The distributed data-plane testing tool built for OpenStack.
Read the documentation.
SonarQube
A SonarQube Docker container enforces source code quality. As part of the Akraino CI build, Jenkins triggers a static source code analysis, storing the results in SonarQube.
Sonobuoy
Sonobuoy is a diagnostic tool that makes it easier to understand the state of a Kubernetes cluster by running a set of Kubernetes conformance tests in an accessible and non-destructive manner.
Source: Github
SR-IOV
The single root I/O virtualization (SR-IOV) interface is an extension to the PCI Express (PCIe) specification. SR-IOV allows a device, such as a network adapter, to separate access to its resources among various PCIe hardware functions.
Source: Microsoft
Tempest
This is a set of integration tests to be run against a live OpenStack cluster. Tempest has batteries of tests for OpenStack API validation, scenarios, and other specific tests useful in validating an OpenStack deployment.
Source: Github
Read the Documentation
Yardstick
Yardstick is a framework to test non functional characteristics of an NFV Infrastructure as perceived by an application.
Source: Github
Read the Documentation